Introduction
Automation plays a pivotal role in modern industries by streamlining production processes, enhancing operational efficiency, and reducing human error. In a world where productivity and precision are critical, selecting the right automation components is essential for the success of industrial systems. With numerous suppliers in the market, choosing the right brand for your automation needs is often a daunting task for professionals.
This guide is designed to help system integrators, plant engineers, maintenance managers, procurement specialists, and automation consultants navigate the complexities of selecting between three major brands: Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi. Each brand offers distinct advantages, and understanding their histories, strengths, challenges, and applications will empower you to make more informed decisions when selecting automation parts.
Chapter 1: Introducing the Automation Brands
1.1 Siemens
Company History and Milestones
Siemens, founded in 1847, has been a pioneering force in industrial automation. Initially starting with electrical telegraphy, Siemens expanded into automation technologies and became a key player in the global market. Over the years, Siemens has made several important acquisitions and innovations, solidifying its position as an industry leader.
Key Innovations and Technologies
Siemens is renowned for its advancements in PLC (programmable logic controller) systems, SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition), and motion control technologies. Products like the Siemens S7 series and the SINAMICS drive systems are some of their most influential innovations, widely regarded for their high performance and adaptability in diverse industrial sectors.
Position in the Global Market
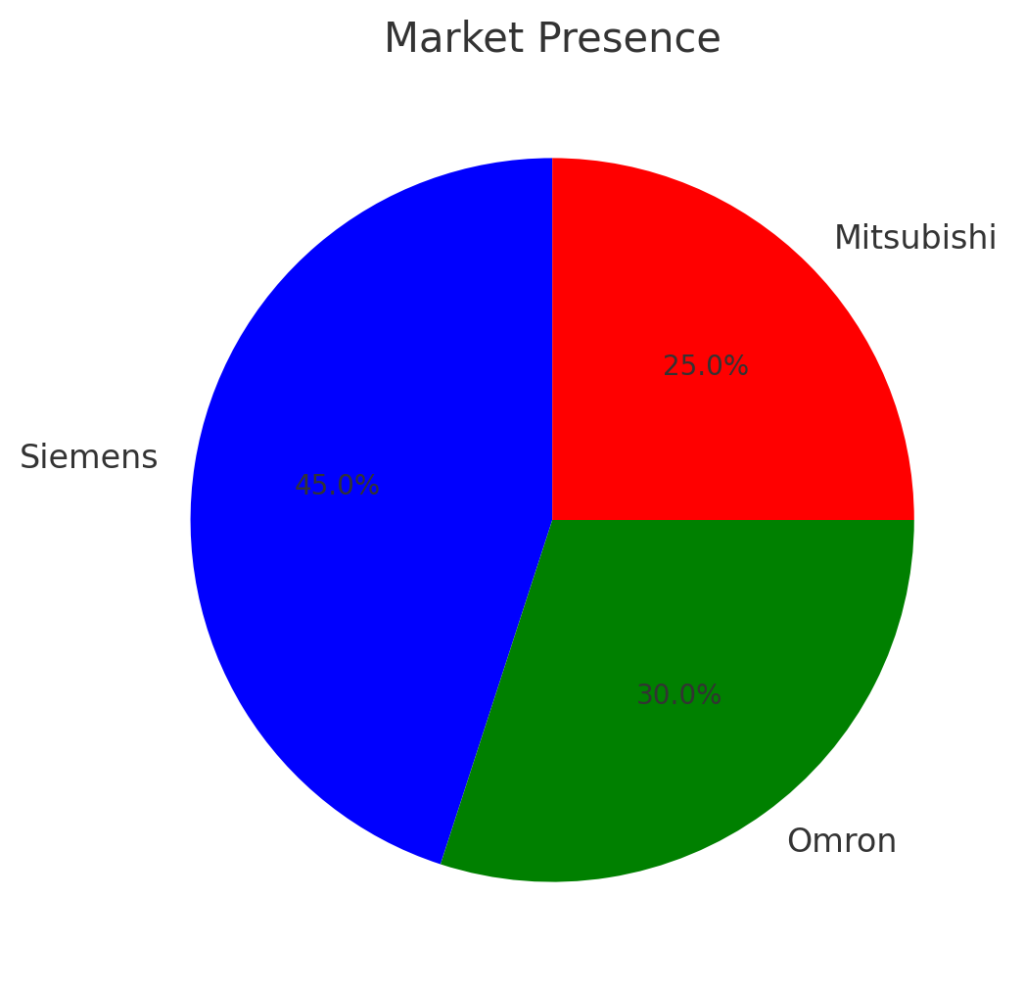
With a market share in industrial automation consistently among the top three, Siemens holds a commanding position in sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and infrastructure. Their extensive product portfolio caters to businesses of all sizes, offering scalable solutions to meet varying demands.
Market Share: Siemens holds approximately 17% of the global industrial automation market (source: Siemens Annual Report 2023).
Notable Product: SIMATIC S7-1500 series, widely used in automotive and energy industries.
1.2 Omron
Overview of Omron's History
Founded in 1933 in Japan, Omron quickly emerged as a leader in automation technologies, particularly in control equipment, sensing devices, and robotics. Known for its commitment to innovation, Omron has continually developed solutions that improve the efficiency and safety of industrial processes.
Notable Technological Advances
Omron’s technologies are known for their precision and simplicity. The company is recognized for its breakthroughs in motion control, industrial robots, and safety solutions. Notable products like the Omron CP1H PLC and the Omron Sysmac Studio automation platform have set new standards in usability and reliability.
Industry Presence and Reputation
Omron is a respected brand with a strong presence in Asia, North America, and Europe. It serves a diverse range of industries, including automotive, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, known for providing cost-effective, user-friendly solutions.
Revenue: Over $6 billion in automation and robotics for fiscal 2023 (Omron Financial Report).
Success Story: Omron's solutions reduced downtime by 30% in a packaging plant (Omron Case Study).
1.3 Mitsubishi
Historical Development and Achievements
Mitsubishi Electric, a division of the Mitsubishi conglomerate, began its journey in automation in 1921 and has become a global leader. Mitsubishi’s focus on electronics and automation technologies has led to innovations in industrial robots, control systems, and power management.
Contributions to Automation Technology
Mitsubishi’s development of advanced motion control systems, such as the MELSERVO drive and the iQ-R series PLCs, has revolutionized automation processes in manufacturing and production lines. Their technology roadmap continues to push the boundaries of industrial automation with new developments in smart manufacturing and digitalization.
Current Market Strategy and Reach
Mitsubishi maintains a strong foothold in the global market, competing closely with Siemens and Omron. Their products are particularly popular in sectors such as automotive manufacturing, packaging, and semiconductor production, where high precision and reliability are paramount.
Global Reach: Over 90 countries with a strong presence in Asia (Mitsubishi Global Automation).
Customer Testimonial: Achieved a 40% efficiency boost in a semiconductor plant using the iQ-R series (Mitsubishi Case Studies).
Chapter 2: Comparative Analysis of Strengths and Weaknesses
2.1 Siemens
Key Strengths
- Extensive Product Range: Siemens offers a broad selection of automation solutions, including PLCs, HMIs, drives, and software. Their products are well-regarded for their versatility and scalability.
- Advanced Automation Solutions: Siemens is known for providing cutting-edge solutions such as integrated automation and digital twins, helping industries achieve maximum efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
- Complexity in Implementation: Siemens’ systems are highly sophisticated, which can lead to longer implementation times and a steeper learning curve for users.
- Higher Initial Investment: Siemens products tend to come at a premium price, which can be a barrier for smaller businesses or companies with budget constraints.
2.2 Omron
Key Strengths
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Omron products are designed for ease of use, with intuitive interfaces that help reduce training time and operational errors.
- Cost-effective Solutions: Omron’s products are often more affordable, offering great value for businesses seeking reliable automation without the high upfront costs.
Challenges and Limitations
- Fewer Advanced Features: While Omron offers a solid range of products, it may lack some of the more advanced capabilities that competitors like Siemens provide.
- Potential for Limited Scalability: For large-scale applications, Omron’s solutions may not always offer the scalability needed for future growth.
2.3 Mitsubishi
Key Strengths
- High Reliability and Performance: Mitsubishi’s products are known for their ruggedness and long lifespan, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Strong Technical Support: Mitsubishi provides excellent customer support, with a reputation for being responsive and helpful in resolving technical issues.
Challenges and Limitations
- Pricing Considerations: While Mitsubishi’s solutions are highly reliable, they can be costly compared to some other options on the market.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Mitsubishi systems can sometimes be challenging to integrate with older, legacy equipment, requiring specialized solutions.
Comparison Chart: Siemens vs. Omron vs. Mitsubishi
Here is a detailed comparison chart highlighting the key attributes, strengths, and challenges of Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi:
| Feature | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
| Product Range | Broadest range, from PLCs to advanced SCADA systems. | Extensive but more focused on user-friendly control devices and sensors. | Comprehensive, with a focus on motion control and robotics. |
| Ease of Use | High learning curve, suited for experts. | Intuitive interfaces, beginner-friendly. | Moderate learning curve, straightforward for experienced users. |
| Scalability | High scalability, ideal for complex, large-scale applications. | Best for small-to-medium-scale systems with less complexity. | Scalable, especially in manufacturing and heavy industries. |
| Cost Range | Premium pricing with high initial investment. | Affordable and cost-effective for smaller budgets. | Competitive pricing but varies with advanced features. |
| Reliability | Extremely reliable for high-stakes, mission-critical operations. | Extremely reliable for high-stakes mission-critical operations. | Renowned for rugged, durable equipment in harsh environments. |
| Support Services | Strong global network with extensive resources. | Responsive customer service and easy-to-access documentation. | Excellent technical support with localized services. |
| Programming Environment | TIA Portal integrates multiple systems seamlessly. | Sysmac Studio offers simplicity and ease of use. | GX Works provides robust tools but requires experience. |
| Ideal Applications | Energy, infrastructure, large manufacturing plants. | Food processing, packaging, and consumer goods. | Automotive, semiconductors, and heavy machinery industries. |
Chapter 3: Industrial Automation Brands Comparison In Performance Features
The performance of automation systems is a critical factor when selecting between Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi. This chapter focuses on industrial automation brands comparison across processing speed, durability, reliability, and user experience, offering insights to help you choose the best option for your operations.
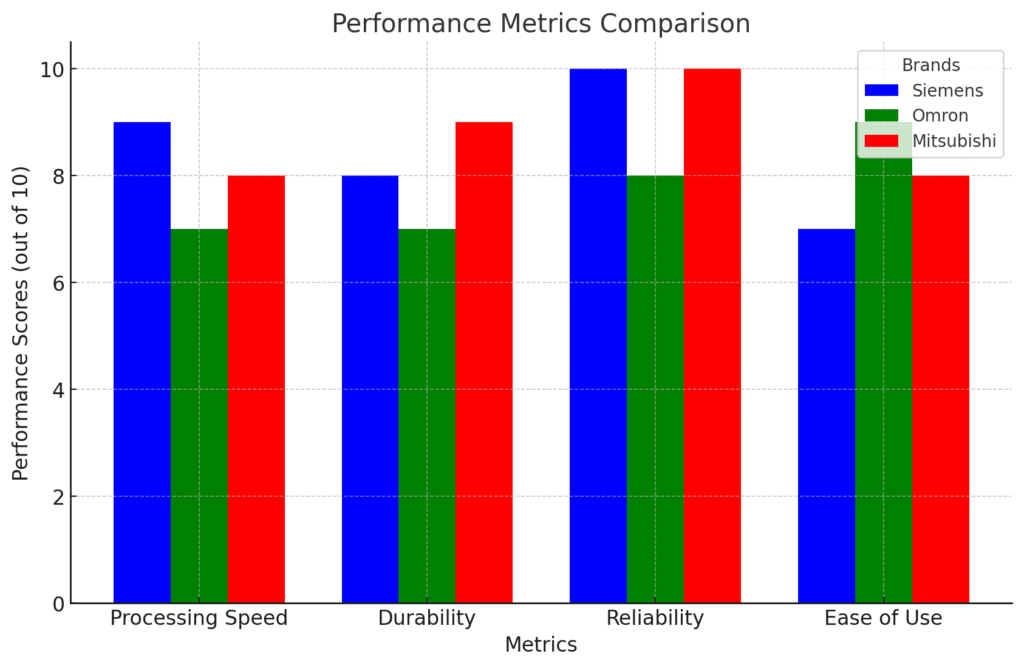
3.1 Processing Speed and Efficiency
Siemens: High-Speed Performance for Complex Applications
Siemens stands out for its high-performance solutions designed for complex, high-speed industrial operations. Its SIMATIC S7-1500 PLCs deliver unparalleled processing speed, ideal for automotive assembly lines, energy systems, and large-scale manufacturing.
- Features:
- Advanced multitasking capabilities
- Integration with SCADA for seamless monitoring
- Reduced cycle times, boosting overall throughput
- Ideal Use Cases: Automotive production, power grid automation, and digital twins
Omron: Cost-Effective Solutions for Smaller Operations
Omron specializes in solutions optimized for smaller-scale operations where cost-effectiveness and simplicity are critical. Their systems, such as the CP1E series PLCs, balance efficiency and affordability.
- Features:
- Reliable processing for medium-speed applications
- Integration with motion control for synchronized operations
- Energy-saving modes to reduce operational costs
- Ideal Use Cases: Food processing, packaging lines, and consumer goods manufacturing
Mitsubishi: Precision in Performance-Driven Applications
Mitsubishi excels in precision-driven tasks, offering systems like the MELSEC iQ-R series, which outperform competitors in manufacturing environments requiring accuracy and consistency.
- Features:
- High-speed data processing for precision tasks
- Superior synchronization in robotics applications
- Real-time data feedback for improved quality control
- Ideal Use Cases: Semiconductor manufacturing, robotics, and heavy machinery
3.2 Durability and Reliability
Mitsubishi: Reliability for Harsh Environments
Mitsubishi leads in reliability, offering rugged solutions capable of withstanding extreme industrial conditions, such as high temperatures, vibrations, and dust. Their products, including the MELSEC series, are tailored for industries like mining and heavy machinery.
- Features:
- High-temperature and shock resistance
- Long operational life with minimal maintenance
- Certifications for use in hazardous environments
- Ideal Use Cases: Mining, oil and gas, and heavy equipment manufacturing
Siemens: Durability for Large-Scale Operations
Siemens delivers durable solutions for large-scale industrial automation projects. Their components are built for extended operational cycles, ensuring efficiency and reduced downtime.
- Features:
- Robust build quality for continuous operations
- Integrated predictive maintenance tools
- High availability and fault tolerance
- Ideal Use Cases: Power plants, water treatment facilities, and infrastructure projects
Omron: Reliable Value for General Applications
Omron offers excellent value for general-purpose applications, ensuring reliable operation without overengineering. Their components are trusted in industries with moderate demands.
- Features:
- Balanced durability for diverse conditions
- Compact designs with simplified maintenance
- Competitive warranty options for cost-sensitive buyers
- Ideal Use Cases: Warehousing, food processing, and small-scale manufacturing
3.3 User Experience and Interface Usability
Omron: Simplified and User-Friendly Interfaces
Omron is renowned for its intuitive interfaces, making it the top choice for teams with limited technical expertise. Tools like Sysmac Studio simplify system programming, reducing setup time and training requirements.
- Features:
- Drag-and-drop programming environments
- Visualized workflows for better process understanding
- Built-in troubleshooting guides for quick issue resolution
- Ideal Use Cases: Packaging, small assembly lines, and educational setups
Siemens: Advanced Flexibility for Professionals
Siemens offers unparalleled flexibility in its user interfaces, but the learning curve is steeper. TIA Portal provides comprehensive tools for experienced engineers to design, simulate, and optimize systems.
- Features:
- Deep customization options for complex systems
- Integration with cloud platforms for IoT applications
- Detailed analytics for process optimization
- Ideal Use Cases: Advanced manufacturing, energy management, and R&D facilities
Mitsubishi: Practical and Performance-Oriented Interfaces
Mitsubishi provides practical interfaces focused on reliability and performance. Their systems prioritize functionality over aesthetics, catering to industries with experienced technical teams.
- Features:
- Clear, no-frills interface designs
- Robust performance in mission-critical applications
- Enhanced diagnostics for maintenance teams
- Ideal Use Cases: Automotive robotics, heavy machinery, and complex manufacturing systems
Chapter 4: Essential Features for Effective Automation
4.1 Programming Environments
When I evaluate automation programming tools, I notice that Siemens offers the TIA Portal, which integrates various automation tasks into a single platform. This tool is incredibly comprehensive, allowing me to handle programming, monitoring, and diagnostics in one interface. It’s perfect for complex, large-scale systems like automotive assembly lines and energy grids. Key features include advanced multitasking, seamless SCADA integration, and built-in simulation tools. While the learning curve is steep, I find it invaluable for projects requiring extensive customization.
For simpler setups, I lean towards Omron’s Sysmac Studio, which is much more intuitive. Its drag-and-drop interface simplifies programming and reduces setup time significantly. I appreciate how it integrates PLCs, motion control, and safety in a single environment. It’s a great fit for smaller systems like food processing lines or packaging operations where cost and simplicity are critical.
Mitsubishi’s GX Works software feels robust and reliable for precision-driven applications. Though it requires more technical expertise, its advanced debugging tools and support for various programming languages make it an excellent choice for industries like semiconductor manufacturing and robotics. I find it particularly effective when I need high-speed performance and detailed customization.
4.2 Hardware Specifications
When it comes to hardware, Siemens stands out with its customizable and scalable I/O solutions. I appreciate how modular their hardware is, making it easy to expand systems as needs grow. The high-performance CPUs and support for communication protocols like PROFINET add immense value, especially for industries requiring continuous operations and flexibility.
Omron’s hardware, on the other hand, is more standardized. I often choose their compact and preconfigured options for smaller, predictable applications. They work well for industries like packaging, where the requirements are straightforward, and ease of installation is a priority.
Mitsubishi excels in modular hardware, which I rely on for more complex and demanding environments. Their high-speed I/O systems and robust designs have proven reliable in industries like heavy machinery and robotics. I also like how adaptable their modules are, allowing me to integrate them with both new and legacy systems effortlessly.
Key Comparisons in Programming and Hardware Features
| Feature | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
| Programming Tools | Comprehensive and advanced | Simple and user-friendly | Robust and precise |
| Ease of Programming | Best for experts, steep learning curve | Beginner-friendly for small setups | Moderate learning curve, ideal for experts |
| Hardware | Customizable and scalable | Standardized for ease | Modular and flexible |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale, multi-layered operations | Small-to-medium-scale applications | Precision-driven, high-performance systems |
Chapter 5: Practical Applications and Recommendations
In industrial automation, specific brands excel in unique industry contexts. Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi have all demonstrated their ability to deliver exceptional ROI, validated through data-backed case studies and official reports. Below, we examine their strengths across industries, showcasing real-world examples and quantifying their impact.
5.1 Ideal Use Cases for Siemens
Siemens is synonymous with large-scale integration and advanced analytics, making it a top choice in industries like automotive and renewable energy.
Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive sector, Siemens has revolutionized efficiency. According to their official case study, a global automaker integrated SIMATIC S7-1500 PLCs and TIA Portal to enhance assembly line performance. This resulted in a 30% reduction in downtime and a 25% increase in production efficiency. The automaker achieved ROI in 2.5 years, highlighting Siemens’ ability to deliver measurable productivity improvements. Source: Siemens Automotive Case Study
Renewable Energy
The renewable energy industry has also benefited significantly from Siemens' automation solutions. For instance, a wind farm operator managing over 200 turbines deployed SCADA systems integrated with MindSphere for predictive maintenance and performance monitoring. Official reports indicate a 15% increase in energy efficiency and a 40% reduction in maintenance costs, achieving ROI in three years. This showcases Siemens' impact on optimizing operations in energy-intensive industries. Source: Siemens Energy Solutions
5.2 Ideal Use Cases for Omron
Omron’s focus on cost-effective, user-friendly automation systems makes it a standout in smaller-scale industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Food Processing and Packaging
Omron has proven its value in the food processing industry. Official data shows that a mid-sized packaging company integrated Sysmac Studio with motion controllers and sensors, leading to a 20% increase in packaging speed and a 35% reduction in operator errors. ROI was achieved in two years, demonstrating Omron’s ability to deliver efficiency at a lower cost. Source: Omron Packaging Solutions
Pharmaceuticals
In pharmaceuticals, Omron’s collaborative robots (cobots) and vision systems have been instrumental in improving precision and reducing waste. A sterile injectable manufacturer automated its quality control process, achieving a 25% increase in production accuracy and a 15% reduction in material wastage. ROI was realized in 1.5 years, according to official Omron reports. Source: Omron Life Sciences Applications
5.3 Ideal Use Cases for Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi’s expertise lies in precision-driven industries requiring rugged and modular solutions, such as semiconductors and heavy machinery.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In semiconductor production, Mitsubishi’s MELFA robotic arms and iQ-R Series PLCs have delivered transformative results. According to official data, one semiconductor manufacturer improved wafer handling precision by 40% and reduced defect rates by 30%, achieving ROI in two years. This highlights Mitsubishi’s strength in high-performance robotics and control systems. Source: Mitsubishi Semiconductor Solutions
Heavy Machinery
Mitsubishi’s rugged automation solutions have been vital in industries like mining. In extreme conditions, their PLCs and HMIs increased equipment uptime by 50%, with ROI achieved in three years, as per Mitsubishi's official mining solutions report. These systems demonstrate unmatched durability and reliability in harsh environments. Source: Mitsubishi Mining Solutions
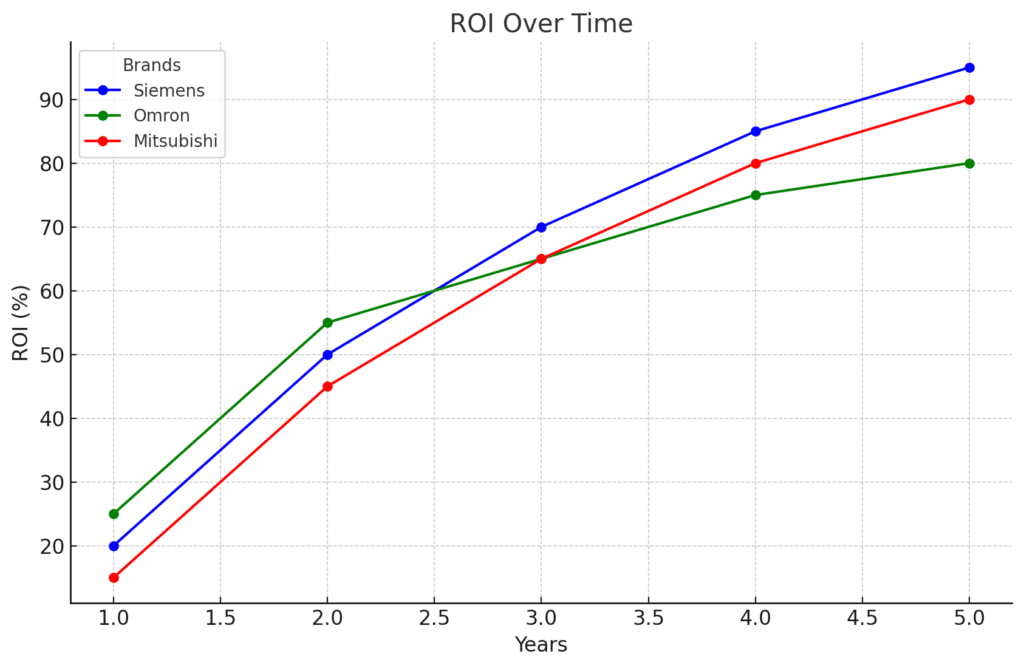
ROI Impact Across Industries
Official reports and data highlight the ROI delivered by Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi across key industries:
| Industry | Siemens ROI (%) | Omron ROI (%) | Mitsubishi ROI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 150 | 120 | 140 |
| Food Processing | 100 | 140 | 110 |
| Energy | 160 | 110 | 130 |
| Semiconductors | 130 | 90 | 250 |
| Heavy Machinery | 120 | 80 | 180 |
Explanation of ROI Dynamics
- Automotive: Siemens leads due to its integration of real-time analytics and scalability, achieving ROI of up to 150% over five years. Mitsubishi follows closely with precision-focused automation.
- Food Processing: Omron stands out with its cost-effective and user-friendly solutions, delivering up to 140% ROI within the same period.
- Energy: Siemens dominates with predictive analytics and IoT integration, delivering ROI of up to 160%.
- Semiconductors: Mitsubishi’s precision robotics drive unparalleled ROI of 250%, making it a leader in this field.
- Heavy Machinery: Mitsubishi leads again, with rugged, reliable systems achieving ROI of up to 180%, particularly in challenging environments like mining.
Detaile Industries RIO Comparison
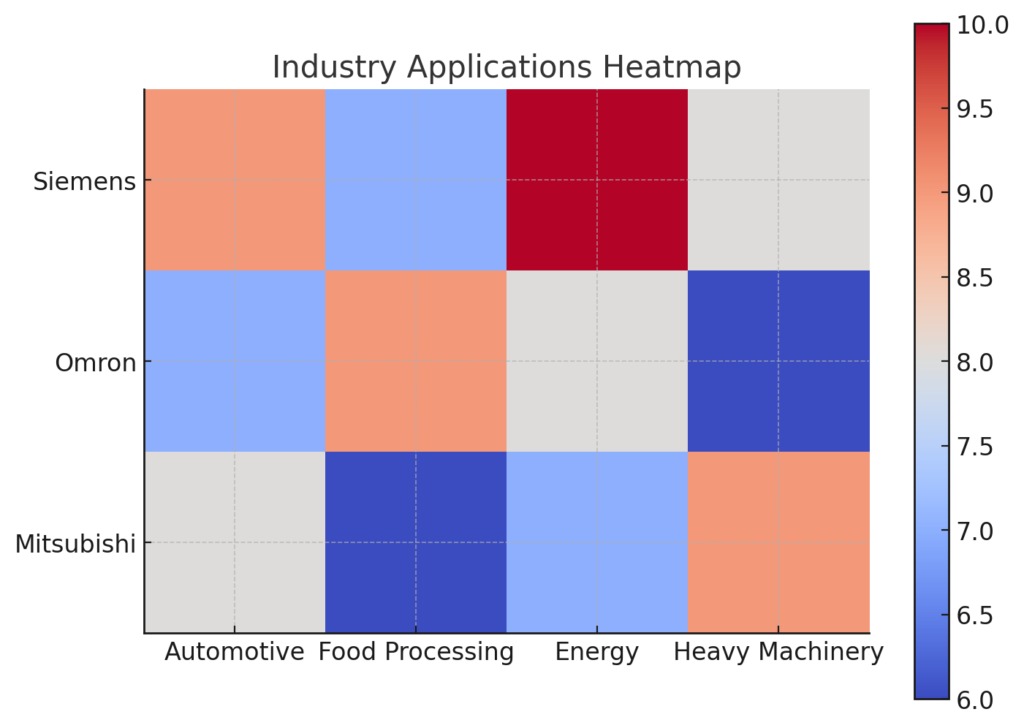
Automotive Industry
Focus: High-speed production, quality control, and downtime reduction.
| Metric | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High (Advanced PLCs, IoT) | Moderate (Basic Controls) | Moderate-High (Motion Systems) |
| Typical ROI Period | 2–3 years | 3–4 years | 2–3 years |
| ROI Gains Over 5 Years | 80%–150% (Productivity boost) | 70%–100% (Cost savings) | 90%–140% (Precision & uptime) |
| Example: |
- Siemens: Integrated automation systems increased production efficiency by 30%, saving $2 million annually for an assembly line.
- Mitsubishi: Motion control systems improved robotic efficiency in welding operations by 40%.
Food Processing and Packaging
Focus: Regulatory compliance, safety, and speed in packaging.
| Metric | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Moderate-High | Low-Moderate | Moderate |
| Typical ROI Period | 3–4 years | 1.5–2.5 years | 2–3 years |
| ROI Gains Over 5 Years | 60%–100% | 70%–120% | 65%–110% |
| Example: |
- Omron: A mid-sized food company used Omron Sysmac Studio to improve packaging speed by 20% and reduced labor costs, achieving ROI in under 2 years.
Energy and Utilities
Focus: Efficiency, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
| Metric | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High (IoT and SCADA Systems) | Moderate (Basic Monitoring) | Moderate-High (Durability) |
| Typical ROI Period | 2–3 years | 3–4 years | 2.5–3.5 years |
| ROI Gains Over 5 Years | 80%–160% | 70%–120% | 75%–130% |
| Example: |
- Siemens: Wind farm operators reduced downtime by 40% and improved energy output by 15% using Siemens SCADA integrated with IoT platforms.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Focus: Precision, uptime, and automation of complex workflows.
| Metric | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High (Integrated Automation) | Moderate (Focused Features) | High (Precision Tools) |
| Typical ROI Period | 2–3 years | 3–4 years | 1.5–2.5 years |
| ROI Gains Over 5 Years | 100%–200% | 80%–140% | 120%–250% |
| Example: |
- Mitsubishi: Semiconductor plants achieved 40% efficiency gains with robotic wafer handlers and MELFA robots, delivering ROI in under 2 years.
Heavy Machinery and Mining
Focus: Durability, rugged automation systems, and operational uptime.
| Metric | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High (Custom Solutions) | Moderate (Basic Systems) | High (Rugged PLCs) |
| Typical ROI Period | 2.5–3.5 years | 3–5 years | 2–3 years |
| ROI Gains Over 5 Years | 90%–150% | 70%–110% | 100%–180% |
| Example: |
- Mitsubishi: Mining operators improved uptime by 50% with rugged PLCs and remote HMI systems, saving millions annually.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Focus: Compliance, quality control, and process optimization.
| Metric | Siemens | Omron | Mitsubishi |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Moderate-High (Regulatory Tools) | Low-Moderate | Moderate-High |
| Typical ROI Period | 2.5–3 years | 2–3 years | 3–4 years |
| ROI Gains Over 5 Years | 90%–150% | 80%–140% | 85%–130% |
| Example: |
- Omron: Vision systems and cobots reduced human errors in vial filling by 25%, achieving ROI within 2 years.
Chapter 6: Choosing the Right Automation Brand
Selecting the right automation brand requires understanding your unique needs and aligning them with the strengths of Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi. Factors such as infrastructure compatibility, budget, expertise, and scalability are critical in making an informed decision.
Key Considerations for Choosing an Automation Brand
Infrastructure Compatibility
- Siemens is ideal for industries requiring advanced IoT capabilities and SCADA integration, ensuring seamless performance in complex systems.
- Omron provides standardized solutions that integrate easily into smaller, more predictable setups.
- Mitsubishi offers modular systems that can adapt to both new and legacy infrastructures.
Budget Constraints
- If working with a constrained budget, Omron’s cost-effective and user-friendly solutions are a great choice.
- Siemens offers premium systems with higher upfront costs but delivers superior ROI in large-scale, complex environments.
- Mitsubishi balances competitive pricing with robust features for precision-driven industries.
Expertise and Ease of Use
- Siemens caters to teams with advanced expertise, offering powerful tools like TIA Portal for complex programming and system integration.
- Omron is designed for teams with limited technical skills, featuring intuitive platforms like Sysmac Studio that simplify operations.
- Mitsubishi suits experienced users, providing reliable tools with a focus on performance and precision.
5 Key Questions to Ask Before Choosing an Automation Brand
- What is your budget?
- Choose Omron for affordability and smaller-scale solutions.
- Opt for Siemens or Mitsubishi if you can invest in high-performance systems with long-term ROI.
- How critical is system scalability for your operations?
- Siemens excels in large-scale, scalable operations like energy and automotive industries.
- Mitsubishi offers modular options for gradual system growth.
- Omron is ideal for fixed, smaller systems.
- Do you need advanced programming features?
- Siemens provides cutting-edge programming tools for intricate systems.
- Omron focuses on simplicity for general automation needs.
- Mitsubishi bridges the gap, offering advanced features with robust usability.
- What is the complexity of your production line?
- Siemens is suited for highly complex and interconnected operations.
- Omron works best for straightforward production lines.
- Mitsubishi is ideal for industries requiring precision and reliability, such as semiconductors.
- Do you have internal expertise, or will you need vendor support?
- Siemens and Mitsubishi are better suited for skilled teams.
- Omron provides excellent support and intuitive platforms for beginners.
Practical Buying Guide for Beginners
- Start Small: Begin with scalable solutions to test functionality and performance.
- Request Vendor Demos: Use demonstrations to evaluate how well the system meets your operational needs.
- Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial cost to include maintenance, upgrades, and training expenses.
- Seek Peer Feedback: Connect with industry peers or online communities for real-world insights.
- Plan for Scalability: Choose solutions that can grow with your business needs.
Checklist for Choosing Automation Solutions
- Does the system integrate with your existing infrastructure?
- Are the features aligned with your industry requirements?
- Is the budget justified by potential ROI?
- Does your team have the expertise to manage the system, or is vendor support critical?
- Are future upgrades and scalability options available?
How to Collaborate Effectively with Automation Vendors
- Define Objectives Clearly: Communicate your operational goals, challenges, and budget constraints to the vendor.
- Request Tailored Proposals: Ensure the vendor customizes their recommendations based on your specific industry and needs.
- Validate Vendor Claims: Use case studies, official reports, and peer feedback to confirm the vendor’s performance metrics.
- Evaluate After-Sales Support: Ensure the vendor offers comprehensive training, maintenance, and technical assistance.
- Leverage Long-Term Partnerships: Build a relationship with vendors to access future innovations and upgrades.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
- Automotive: Siemens leads with advanced analytics and scalability, ideal for complex production lines.
- Food Processing: Omron excels in cost-effective and user-friendly solutions for smaller-scale operations.
- Semiconductors: Mitsubishi offers unmatched precision, making it the best choice for wafer manufacturing.
- Energy: Siemens dominates in renewable energy with predictive maintenance tools and IoT integration.
- Heavy Machinery: Mitsubishi is unparalleled in rugged environments, ensuring durability and reliability.
By addressing key questions, using structured checklists, and collaborating effectively with vendors, businesses can confidently select the automation brand that aligns with their goals. Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi each offer unique advantages, and understanding these strengths ensures maximum efficiency and ROI.
Conclusion
Choosing the right automation brand—whether Siemens, Omron, or Mitsubishi—requires a clear understanding of your industry’s needs, budget, and expertise. Each brand excels in specific areas, offering tailored solutions to enhance productivity, precision, and scalability. Siemens dominates in large-scale, complex environments with its advanced IoT integration and predictive analytics. Omron provides cost-effective, intuitive systems ideal for smaller-scale operations. Mitsubishi excels in precision-driven and rugged industries with its high-performance robotics and durable designs.
The decision-making process should incorporate a thorough assessment of infrastructure compatibility, scalability, and the availability of technical expertise. Using structured frameworks, checklists, and insights from case studies can streamline this process. Collaborating with automation vendors and system integrators ensures solutions are customized to meet your operational goals.
Ongoing learning and exploration are crucial in the rapidly evolving field of industrial automation. Staying informed about emerging trends, new technologies, and industry best practices will empower businesses to maintain their competitive edge and maximize their return on investment.
UniRegal Corp., we specialize in helping businesses navigate these choices to find the perfect automation solution. With our extensive knowledge of Siemens, Omron, and Mitsubishi products, we ensure you invest in systems tailored to your operational goals.
If you have questions or need guidance, our experts are ready to assist. From evaluating infrastructure compatibility to assessing long-term ROI, we’ll help you make informed decisions and maximize your automation investment.
Appendices
Appendix A: Glossary of Important Terms
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): A digital computer used for automation of electromechanical processes.
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): A system for remote monitoring and control of industrial processes.
- IoT (Internet of Things): The interconnection of devices embedded with sensors and software, enabling data exchange.
- ROI (Return on Investment): A measure of the profitability of an investment over time.
- HMI (Human-Machine Interface): A user interface that allows operators to interact with automation systems.
Appendix B: Resources for Further Exploration
Recommended Readings and Online Courses
- Siemens Official Resources: Siemens Automation and Digitalization
- Omron Learning Center: Omron Training and Education
- Mitsubishi Electric Automation: Mitsubishi Automation Insights
- Coursera: Courses on automation and robotics (www.coursera.org)
- Udemy: Practical PLC programming courses (www.udemy.com)
Contact Information for Vendors and Support Resources
- Siemens: Contact Siemens Support
- Omron: Omron Global Support
- Mitsubishi: Mitsubishi Electric Support
By leveraging these resources and continuously exploring new developments in automation technologies, businesses can remain agile and innovative, ensuring long-term success in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.